What is Oncology?
Oncology

What is Oncology?
Oncology is the branch of science that studies tumors and also means cancer science. Oncology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of tumors, which are divided into benign and malignant types, and also covers cancer prevention, cancer screening, and early diagnosis applications. Biopsy and pathological evaluation, which have an important place in cancer diagnosis, are essential for oncology. In biopsy, a tissue sample is taken from a tumor suspected of cancer. The tissue sample taken in biopsy is examined under a microscope during pathological evaluation.
According to research conducted in our country, breast, thyroid, bowel, uterine, and lung cancers are most commonly seen in women, while lung, prostate, bowel, bladder, and stomach cancers are seen in men.
What sciences does oncology cover?
Cancer is the uncontrolled proliferation of cells. It is a disease that causes dysfunction of the organ or system where cancer cells are located. Therefore, differences can be observed in patients regarding the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of the disease. Due to the differences observed in cancer diagnosis and treatment, oncology patients are managed in a multidisciplinary manner by many specialty branches. Other specialty areas involved in cancer treatment are surgical oncology, medical oncology, and radiation oncology. With the collaboration of many specialty branches, patients’ treatment can be monitored more closely. Surgical oncology, which plays an active role in diagnosing the disease, is also effective in removing the tumor from the body. General surgery, ear-nose-throat, neurosurgery, thoracic surgery, orthopedics, etc. surgical disciplines are included in this group. Drug and radiotherapy treatment can be applied after cancer treatment as well as in those with advanced disease unsuitable for surgery. Drug treatment is applied by Medical Oncology, and radiotherapy treatment is applied by Radiation Oncology. If the person to receive cancer treatment is a child, the treatment is performed by Pediatric Oncology.
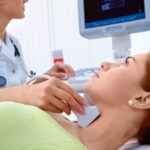
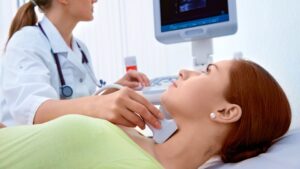
How is diagnosis made?
The most important diagnostic method in oncology is the person’s clinical history. Other common symptoms that indicate cancer are:
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Unexplained anemia
- Fever of unknown origin
- Palpable masses
- New onset and worsening complaints
can be listed.
How is cancer treated?
Cancer has many types and stages. Treatment can also vary according to the type and stage of cancer. Among the main cancer treatments used in oncology:
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Immunotherapy
- Hormone therapy
- Molecular therapies
- Stem cell transplants
- Minimally invasive applications
are commonly used.
Chemotherapy
One of the specialty areas used in cancer treatment is Medical Oncology. Medical Oncology performs chemotherapy applications. Chemotherapy is the name given to drug treatment of cancer. Treatment varies according to the type of cancer and can be administered intravenously or orally. Cancer planning differs according to cell type, the organ where it started, and the area it tends to spread.
For what purpose is chemotherapy performed?
Chemotherapy can be performed for many purposes in cancer treatment. Among these:
- To shrink the tumor before surgical operation
- For protective purposes after surgical operation
- Before, after, or together with radiotherapy, which is one of the local treatment methods
are included. Chemotherapy aims to eliminate uncontrollably growing cancer cells. While chemotherapy is applied in effective doses to achieve the intended treatment results, possible side effects are also controlled.
What types of cancer are treated in Medical Oncology?
There are many types of cancer. These include:
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Stomach-bowel cancers
- Pancreatic cancer
- Liver cancer
- Gallbladder and bile duct cancers
- Head-neck tumors
- Osteosarcoma and soft tissue sarcomas
- Brain tumors
- Kidney-bladder cancers
- Prostate cancer
- Malignant melanoma
- Thyroid cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Uterine cancer
- Testicular cancer
- Lymphomas
- Multiple myeloma
such cancer types can be listed.
What is radiotherapy?
Another name for radiotherapy is radiation therapy. Cancer disease is treated with the help of ionizing radiation. The main principle of radiotherapy is based on killing cancer cells with high levels of radiation or breaking them into pieces to prevent their proliferation. Radiotherapy, which is effective in rapidly spreading cancer cells, is accepted as a targeted treatment approach. In radiation therapy, focus is placed on the tumor area and high-dose radiation is sent to this region.
In which cancer treatments is radiotherapy used?
Radiotherapy has become a priority option for many cancer types today. Radiotherapy protects other organs due to its feature of being applied in a targeted manner to the tumor area. Therefore, it gives successful results when applied alone to gynecological cancers, head and neck cancers, and prostate cancers. In brain tumors, it can be applied alone to eliminate small-sized lesions after surgical operation. Radiotherapy, which is preferred in almost all cancer treatments today, is the only method applied in some cancer types. Radiotherapy is recommended as supportive to treatments such as surgical procedures and chemotherapy in the vast majority of cancer patients.
Cancer types where radiotherapy is most preferred:
- Skin cancer
- Head and neck cancers
- Brain tumors
- Breast cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Bladder cancer
- Gynecological cancers
- Lung cancer
- Soft tissue tumors
- Bone tumors
- Digestive system cancers
- Lymphomas
- Childhood tumors
can be specified.
Does it affect sexual life?
Among the most curious and frequently asked questions is whether radiotherapy affects sexual life. During radiation therapy, patients fall into the misconception that they lose their physical attractiveness due to the side effects of treatment. The problem of sexual reluctance can be solved with psychiatric help. When sexual reluctance is eliminated, it is stated that there is no harm in having sexual intercourse during radiation therapy, except for some gynecological cancers.
What is immunotherapy?
In cancer treatment, immunotherapy is applied alongside chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Immunotherapy is a treatment method based on strengthening the patient’s immune system. Therefore, immunotherapy is also called biological therapy or biotherapy. Cancer cells are destroyed by strengthening the person’s immune system. The immune system detects and attacks cancer cells, preventing the development of these cells. Of course, this is not always a situation that can occur because some cancer cells can make the body’s defense mechanism passive. When the defense mechanism is passive, cancer cells can spread to a larger area by proliferating uncontrollably.
What is hormone therapy?
Hormone therapy can be applied to patients who have completed surgical operations and drug treatments, namely chemotherapies, but whose tumors carry estrogen or hormone receptors. Hormone therapy is based on giving hormone drugs that structurally resemble hormones but have suppressive properties. The drugs used in hormone therapy prevent the effects of estrogen on tumor cells as well as prevent cell proliferation.
What is stem cell transplant?
Blood cells are produced in the bone marrow. Blood-forming stem cells in the bone marrow are responsible for the production of blood cells throughout an individual’s lifetime. Stem cell transplant is also preferred in the treatment of various diseases to benefit from its blood-forming properties.
In the past, since stem cells were collected from bone marrow, bone marrow transplant was performed on patients who would receive stem cell treatment. Today, stem cells can be collected from blood. Therefore, the preference rate for stem cell transplant has increased.
In which cancer types is it used?
Stem cell transplants are mostly used in the treatment of cancer types originating from blood and bone marrow. Cancer types where stem cell transplant is preferred:
- Leukemia
- Multiple myeloma
- Lymphoma
can be given as examples. Before stem cell treatment, stem cells are collected. Stem cells can be collected in three ways. Cells are obtained from the donor’s bone marrow, from circulating blood through vessels, and from the umbilical cord.